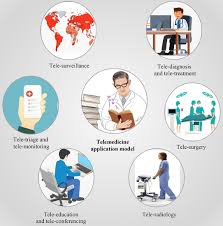
In the realm of modern healthcare, digital health and telehealth are terms that are frequently used interchangeably, but they represent distinct concepts with unique applications. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the nuances between digital health and telehealth, shedding light on their differences and similarities to help you navigate the evolving landscape of healthcare technology.
Table of Contents
What is Digital Health?
digital health and telehealth

Before we delve into the comparison, let’s define digital health. Simply put, digital health encompasses the use of technology to deliver healthcare services, monitor health metrics, and manage medical information. This broad umbrella term encompasses a wide range of applications, including mobile health apps, wearable devices, electronic health records (EHRs), and remote monitoring systems.
Unveiling Telehealth
Similarly, let’s delineate the concept of telehealth. Telehealth specifically pertains to the provision of healthcare services remotely through the utilization of telecommunications technology. This encompasses a myriad of activities, including virtual consultations between patients and healthcare providers, remote monitoring of patients’ health metrics, and the transmission of medical data and images for diagnostic purposes.
Understanding the Disparities
Now that we’ve established the definitions of digital health and telehealth, let’s delve into the key disparities between the two:
Scope and Focus
Digital health exhibits a broader scope, encompassing a wide spectrum of healthcare-related technologies and services beyond the realm of telehealth. It encompasses innovations geared towards promoting wellness, managing chronic conditions, and facilitating patient engagement and education. Telehealth, however, is more narrowly focused on the remote delivery of clinical services, emphasizing virtual consultations and remote monitoring for diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care.
Delivery Mechanism

Another fundamental distinction lies in the delivery mechanism. Digital health solutions are often accessible directly to individuals, empowering them to take an active role in managing their health and wellness. These solutions may include mobile applications, wearable devices, and online platforms that facilitate self-monitoring, health tracking, and access to educational resources. In contrast, telehealth primarily involves interactions between patients and healthcare providers facilitated by telecommunications technology, enabling remote consultations and medical interventions.
Level of Interactivity
While both digital health and telehealth leverage technology to enhance healthcare delivery, they differ in terms of interactivity and user engagement. Digital health solutions often prioritize user-centric design and personalized feedback, empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being. These solutions may offer interactive features, such as real-time health tracking, personalized recommendations, and behavioral coaching. Telehealth, on the other hand, emphasizes real-time interactions between patients and healthcare providers, enabling virtual consultations, remote diagnostics, and treatment planning.
Recognizing Commonalities and Synergies
Despite their disparities, digital health and telehealth share common objectives and often complement each other in advancing healthcare delivery:
Accessibility and Convenience
Both digital health and telehealth aim to enhance accessibility and convenience in healthcare delivery, particularly for individuals facing geographic, mobility, or time constraints. By leveraging technology, patients can access healthcare services from the comfort of their homes, reducing the need for travel and mitigating barriers to care. This is especially beneficial for individuals residing in rural or underserved areas, as well as those with chronic conditions requiring frequent monitoring and management.
H3: Remote Monitoring and Management
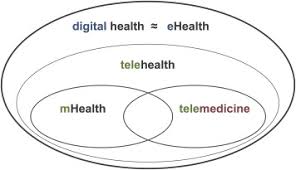
Both digital health and telehealth facilitate remote monitoring of patients’ health status and adherence to treatment plans, enabling proactive intervention and personalized care management. Remote monitoring technologies, such as wearable devices and connected sensors, allow healthcare providers to track patients’ vital signs, medication adherence, and disease progression remotely. This real-time data enables early detection of health issues, timely intervention, and adjustments to treatment plans as needed, thereby improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
What is Telehealth?
Similarly, let’s clarify the concept of telehealth. Telehealth refers specifically to the use of telecommunications technology to deliver healthcare services remotely. This can include virtual consultations between patients and healthcare providers, remote monitoring of patients’ vital signs, and the transmission of medical images and data for diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding the Differences
Now that we have defined both digital health and telehealth, let’s explore the key differences between the two:
Scope of Services

Digital health encompasses a broad spectrum of healthcare-related technologies and services, including but not limited to telehealth. It encompasses everything from mobile health apps that help users track their fitness goals to sophisticated medical devices that monitor chronic conditions. Telehealth, on the other hand, specifically focuses on the delivery of clinical services remotely, such as virtual appointments with healthcare providers.
Mode of Delivery
Another distinction lies in the mode of delivery. Digital health technologies can be accessed and utilized by individuals directly, often through mobile devices or wearable gadgets. Users can track their health metrics, access educational resources, and even communicate with healthcare professionals through these platforms. Telehealth, on the other hand, typically involves interactions between patients and healthcare providers facilitated by telecommunications technology.
Level of Interactivity
While both digital health and telehealth leverage technology to improve healthcare delivery, they differ in terms of interactivity. Digital health solutions often empower individuals to take a proactive role in managing their health, providing personalized feedback and guidance based on user input and data analytics. Telehealth, on the other hand, facilitates real-time interactions between patients and healthcare providers, enabling diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care to be delivered remotely.
Similarities and Complementary Nature
Despite their differences, digital health and telehealth share common goals and often complement each other:
Accessibility and Convenience
Both digital health and telehealth aim to make healthcare more accessible and convenient for patients. By leveraging technology, individuals can access healthcare services from the comfort of their homes, reducing the need for travel and minimizing wait times. This is especially beneficial for individuals with mobility issues, those living in rural or underserved areas, and busy professionals who struggle to find time for in-person appointments.
Remote Monitoring and Management

Both digital health and telehealth enable remote monitoring of patients’ health metrics and conditions. This allows healthcare providers to track patients’ progress, identify potential issues early on, and intervene as needed. For example, wearable devices can continuously monitor vital signs such as heart rate and blood pressure, sending alerts to healthcare providers if any abnormalities are detected.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Healthcare
In conclusion, while digital health and telehealth are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct concepts with unique applications within the healthcare landscape. Digital health encompasses a broad range of technologies aimed at improving healthcare delivery, while telehealth specifically focuses on remote clinical services. By understanding the differences and similarities between the two, healthcare providers and patients alike can harness the power of technology to enhance access, convenience, and quality of care. Whether it’s through digital health apps or telehealth consultations, the future of healthcare is undoubtedly digital.